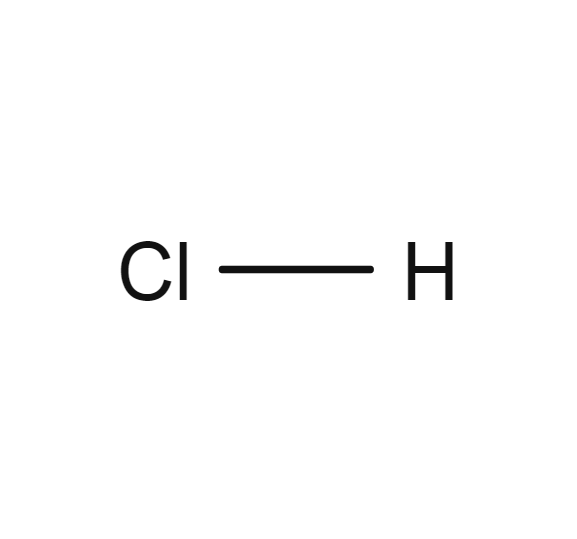
Hydrogen chloride
- HCl
- CAS Number 7647-01-0
- UN1050 (gas)
Click & drag to move the 3D molecule
Liquid / Gas Volumes
Calculate the volume or mass of a quantity of gas or liquid
Liquid Phase
At boiling point at 1.013 bar
Gas Phase
In standard conditions (1.013 bar, 15°C)
Physical Properties
Molecule phase diagram showing the transition phases between solid, liquid and gas as a function of temperature and pressure
-
- Molar mass 36.461 g/mol
- Content in dry air /
-
Critical Point
- Temperature 51.50 °C
- Pressure 83.1 bar
- Density 450.14 kg/m³
-
Triple Point
- Temperature -114.18 °C
- Pressure 1.3522E-1 bar
Pressure 1.013 bar
| Latent heat of fusion (at melting point) | 54.853 kJ/kg |
| Melting point | - 114.18 °C |
Pressure 1.013 bar
| Boiling point | - 85 °C |
| Latent heat of vaporization (at boiling point) | 448.87 kJ/kg |
| Liquid density (at boiling point) | 1192.98 kg/m3 |
| Specific gravity | 1.27 |
| Thermal conductivity | 13.158 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 25.6287 bar |
| Viscosity | 1.3405E-4 Po |
| Gas density (at boiling point) | 2.4329 kg/m3 |
| Gas density | 1.6397 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 764.73 vol/vol |
| Specific gravity | 1.27 |
| Thermal conductivity | 13.924 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 37.3556 bar |
| Viscosity | 1.4164E-4 Po |
| Gas density | 1.5524 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 764.73 vol/vol |
| Specific gravity | 1.27 |
| Thermal conductivity | 14.43 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 47.2216 bar |
| Viscosity | 1.4666E-4 Po |
| Gas density | 1.4993 kg/m3 |
Applications
Examples of uses of this molecule in Industry and Healthcare

Chemicals
The chemicals industry uses hydrogen chloride to produce a large variety of organic chlorinated compounds. Chlorinated metals (such as aluminium or silicon chlorides) are produced with hydrogen chloride.
Electronic components
Hydrogen chloride is used in semiconductor fabrication for etching of native oxide, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) reactor cleaning or moisture getter.

Laboratories & Research Centers
Hydrogen chloride is used in calibration gas mixtures for environmental emission monitoring.

Metal fabrication
Hydrometallurgy processes use hydrogen chloride to enhance the separation coefficient of ores. Hot galvanizing process can use hydrogen chloride.

Other
Used with xenon in "excimer" lasers, hydrogen chloride can produce wavelengths which vary as a function of operating conditions.
Safety & Compatibility
GHS04
Gas under pressure
GHS05
Corrosive
GHS06
Acute Toxicity
Threshold of toxicity
| ILV-15min EU (at Patm and 293.15 K) | 15 mg/m3 or 10 ppm |
| ILV-8h EU (at Patm and 293.15 K) | 8 mg/m3 or 5 ppm |
| PEL USA OSHA (vol) | 5 [ceiling] ppm |
| VLEP CT France (at Patm and 293.15 K) | 7.5 mg/m3 or 5 ppm |
Odor
Pungent and suffocating
Metals
| Aluminium | Not recommended |
| Brass | Not recommended |
| Monel | Satisfactory |
| Copper | No data |
| Ferritic Steel | Satisfactory |
| Stainless steel | Satisfactory |
| Zinc | No data |
| Titanium | No data |
Plastics
| Polytetrafluoroethylene | Satisfactory |
| Polychlorotrifluoroethylene | Satisfactory |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride | Satisfactory |
| Polyvinyl chloride | Satisfactory |
| Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene | No data |
| Polycarbonate | No data |
| Polyamide |
Significant loss of mass
Not recommended
|
| Polypropylene | Satisfactory |
Elastomers
| Butyl (isobutene- isoprene) rubber |
Significant loss of mass
Not recommended
|
| Nitrile rubber |
Significant loss of mass
Not recommended
|
| Chloroprene |
Significant loss of mass
Not recommended
|
| Chlorofluorocarbons | No data |
| Silicone |
Significant loss of mass
Not recommended
|
| Perfluoroelastomers | Satisfactory |
| Fluoroelastomers | Satisfactory |
| Neoprene | No data |
| Polyurethane |
Significant loss of mass
Not recommended
|
| Ethylene-Propylene | Satisfactory |
Lubricants
| Hydrocarbon based lubricant |
Contamination of the material
Not recommended
|
| Fluorocarbon based lubricant |
Contamination of the material
Not recommended
|
Materials compatibility
Learn More
More information
Joseph Priestley prepared hydrogen chloride in 1772 and, in 1818, Humphry Davy established that it is composed of hydrogen and chlorine.