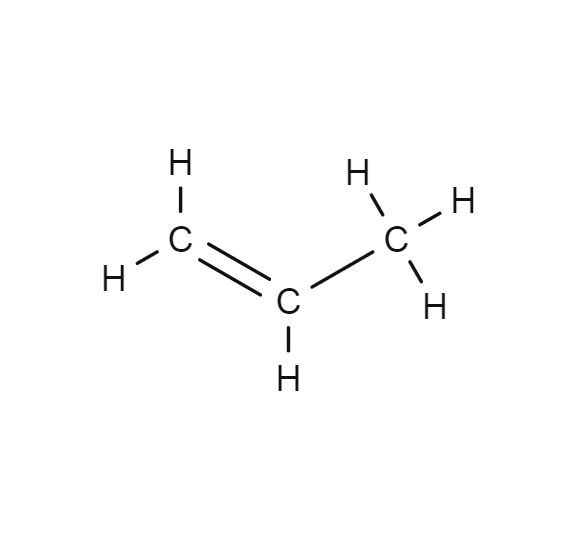
Propene
- C3H6
- CAS Number 115-07-1
- UN1077 (gas)
Click & drag to move the 3D molecule
Liquid / Gas Volumes
Calculate the volume or mass of a quantity of gas or liquid
Liquid Phase
At boiling point at 1.013 bar
Gas Phase
In standard conditions (1.013 bar, 15°C)
Physical Properties
Molecule phase diagram showing the transition phases between solid, liquid and gas as a function of temperature and pressure
-
- Molar mass 42.080 g/mol
- Content in dry air /
-
Critical Point
- Temperature 91.70 °C
- Pressure 46 bar
- Density 227.46 kg/m³
-
Triple Point
- Temperature -185.20 °C
- Pressure 7.4E-9 bar
Pressure 1.013 bar
| Latent heat of fusion (at melting point) | 69.772 kJ/kg |
| Melting point | - 185.26 °C |
Pressure 1.013 bar
| Boiling point | - 47.62 °C |
| Latent heat of vaporization (at boiling point) | 438.96 kJ/kg |
| Liquid density (at boiling point) | 610.06 kg/m3 |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.8094E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.1717 |
| Gas density (at boiling point) | 2.358 kg/m3 |
| Gas density | 1.9134 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 318.84 vol/vol |
| Heat capacity Cp | 1.4643 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 1.2498 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Specific gravity | 1.48 |
| Specific volume | 5.226E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 14.667 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 5.9304 bar |
| Viscosity | 7.813E-5 Po |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.8393E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.1625 |
| Gas density | 1.8083 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 338.23 vol/vol |
| Heat capacity Cp | 1.5139 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 1.3022 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Specific gravity | 1.48 |
| Specific volume | 5.53E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 16.1 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 9.0442 bar |
| Viscosity | 8.2625E-5 Po |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.8559E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.157 |
| Gas density | 1.7447 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 349.66 vol/vol |
| Heat capacity Cp | 1.5482 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 1.338 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Specific gravity | 1.48 |
| Specific volume | 5.732E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 17.095 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 11.6845 bar |
| Viscosity | 8.5599E-5 Po |
Applications
Examples of uses of this molecule in Industry and Healthcare

Chemicals
Propene is the second most important feedstock for the petrochemical industry. Propene is the feedstock in the production of one of the most important polymer: polypropylene. It is also converted to propylene oxide, a precursor of propylene glycol and polyurethane, acrylonitrile, cumene, Oxo-alcohols, Isopropanol and acrylic acid.
Electronic components
Propene is a carbon source for amorphous carbon hard masks.

Laboratories & Research Centers
Propene is used in calibration gas mixtures for petrochemical industry, environmental emission monitoring, industrial hygiene monitors and trace impurity analyzers.
Safety & Compatibility
GHS02
Flammable
GHS04
Gas under pressure
Autoignition Temperature, Flammability Limits & Flash Point
Europe (according to EN1839 for Limits and EN 14522 for autoignition temperature)
| Autoignition temperature (Chemsafe) | 485 °C |
| Lower flammability limit (IEC 80079-20-1) | 2 vol% |
| Upper flammability limit (IEC 80079-20-1) | 11.6 vol% |
US (according to ASTM E681 for Limits and ASTM E659 for autoignition temperature)
| Autoignition temperature (NFPA 325) | 455 °C |
| Lower flammability limit (NFPA 325) | 2 vol% |
| Upper flammability limit (NFPA 325) | 11.1 vol% |
Metals
| Aluminium | Satisfactory |
| Brass | Satisfactory |
| Monel | No data |
| Copper | Not recommended |
| Ferritic Steel | Satisfactory |
| Stainless steel | Satisfactory |
| Zinc | No data |
| Titanium | No data |
Plastics
| Polytetrafluoroethylene | Satisfactory |
| Polychlorotrifluoroethylene | Satisfactory |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride | Satisfactory |
| Polyvinyl chloride |
Significant swelling
Not recommended
|
| Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene | No data |
| Polycarbonate | No data |
| Polyamide | Satisfactory |
| Polypropylene | Satisfactory |
Elastomers
| Butyl (isobutene- isoprene) rubber |
significant swelling
Not recommended
|
| Nitrile rubber |
significant swelling
Not recommended
|
| Chloroprene |
significant swelling
Not recommended
|
| Chlorofluorocarbons | No data |
| Silicone |
Significant swelling
Not recommended
|
| Perfluoroelastomers | Satisfactory |
| Fluoroelastomers | Satisfactory |
| Neoprene | No data |
| Polyurethane |
Significant swelling
Not recommended
|
| Ethylene-Propylene |
significant swelling
Not recommended
|
Lubricants
| Hydrocarbon based lubricant |
significant loss of mass
Not recommended
|
| Fluorocarbon based lubricant | Satisfactory |
Materials compatibility
Learn More
More information
Propene is an unsaturated organic compound. It is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons.