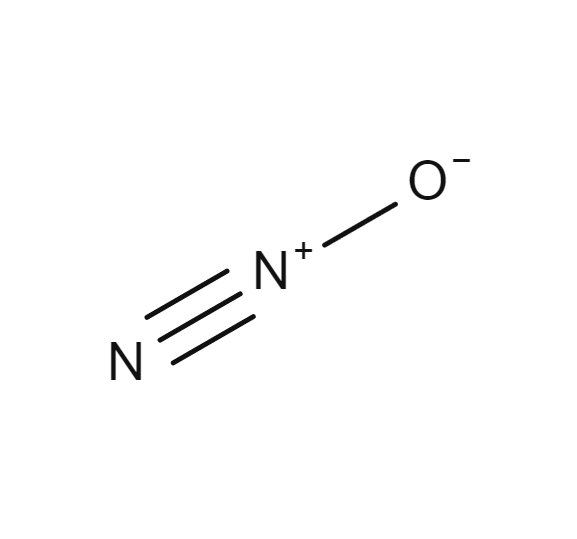
Nitrous oxide
- N2O
- CAS Number 10024-97-2
- UN1070 (gas)
- UN2201 (refrigerated liquid)
Click & drag to move the 3D molecule
Liquid / Gas Volumes
Calculate the volume or mass of a quantity of gas or liquid
Liquid Phase
At boiling point at 1.013 bar
Gas Phase
In standard conditions (1.013 bar, 15°C)
Physical Properties
Molecule phase diagram showing the transition phases between solid, liquid and gas as a function of temperature and pressure
-
- Molar mass 44.013 g/mol
- Content in dry air 0.33 ppm
-
Critical Point
- Temperature 36.42 °C
- Pressure 72.45 bar
- Density 451.88 kg/m³
-
Triple Point
- Temperature -90.82 °C
- Pressure 8.785E-1 bar
Pressure 1.013 bar
| Latent heat of fusion (at melting point) | 148.57 kJ/kg |
| Melting point | - 90.82 °C |
Pressure 1.013 bar
| Boiling point | - 88.47 °C |
| Latent heat of vaporization (at boiling point) | 374.286 kJ/kg |
| Liquid density (at boiling point) | 1230.458 kg/m3 |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.928E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.2933 |
| Gas density (at boiling point) | 2.981 kg/m3 |
| Gas density | 1.9774 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 618.241 vol/vol |
| Heat capacity Cp | 8.5873E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 6.6398E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Specific gravity | 1.53 |
| Specific volume | 5.057E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 16.464 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 32.1176 bar |
| Viscosity | 1.3631E-4 Po |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.9391E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.2853 |
| Gas density | 1.8724 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 652.95 vol/vol |
| Heat capacity Cp | 8.7347E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 6.7959E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Solubility in water | 5.932E-4 mol/mol |
| Specific gravity | 1.53 |
| Specific volume | 5.341E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 17.651 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 45.9221 bar |
| Viscosity | 1.436E-4 Po |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.9453E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.2804 |
| Gas density | 1.8084 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 676.02 vol/vol |
| Heat capacity Cp | 8.8312E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 6.8972E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Solubility in water | 4.386E-4 mol/mol |
| Specific gravity | 1.53 |
| Specific volume | 5.53E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 18.445 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 57.2912 bar |
| Viscosity | 1.4841E-4 Po |
Applications
Examples of uses of this molecule in Industry and Healthcare
Electronic components
In semiconductor and display manufacturing, nitrous oxide can be the oxygen source for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) of silicon oxynitride (doped or undoped) or silicon dioxide.

Food
Nitrous oxide is used as gas propellant for aerosols packaging.

Hospital care
Nitrous Oxide is used in anesthesia or in analgesia

Laboratories & Research Centers
Nitrous oxide is used as fuel gas for the flame in atomic absorption spectrophotometry. It is used in calibration gas mixtures for petrochemical industry, environmental emission monitoring, industrial hygiene monitors and trace impurity analyzers.

Other
Nitrous oxide is used as combustive for the engine of scale models.

Pharma & Biotech
Nitrous oxide is used as gas propellant for aerosols packaging.
Safety & Compatibility
GHS03
Oxidising
GHS04
Gas under pressure
Odor
Sweet
Metals
| Aluminium | Satisfactory |
| Brass |
Risk of stress corrosion cracking
Acceptable
|
| Monel | No data |
| Copper | No data |
| Ferritic Steel | Satisfactory |
| Stainless steel | Satisfactory |
| Zinc | No data |
| Titanium | No data |
Plastics
| Polytetrafluoroethylene | Satisfactory |
| Polychlorotrifluoroethylene | Satisfactory |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride |
Violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Acceptable
|
| Polyvinyl chloride |
Violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
| Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene | No data |
| Polycarbonate | No data |
| Polyamide | Satisfactory |
| Polypropylene |
Violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
Elastomers
| Butyl (isobutene- isoprene) rubber |
Significant swelling, violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
| Nitrile rubber |
Significant swelling, violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
| Chloroprene |
Significant swelling, violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
| Chlorofluorocarbons | No data |
| Silicone | Satisfactory |
| Perfluoroelastomers |
Significant swelling
Not recommended
|
| Fluoroelastomers |
Significant swelling
Not recommended
|
| Neoprene | No data |
| Polyurethane | Satisfactory |
| Ethylene-Propylene |
Significant swelling, violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Acceptable
|
Lubricants
| Hydrocarbon based lubricant |
Violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
| Fluorocarbon based lubricant | Satisfactory |
Materials compatibility
Learn More
More information
The gas was first synthesized by English natural philosopher and chemist Joseph Priestley in 1772, who called it "phlogisticated nitrous air". On Earth, it occurs naturally in soil and oceans. It is produced by the combustion of organic or fossils matters, particularly in industry. The massive use of nitrogen-based chemical fertilizers has contributed to increase the level of nitrous oxide found in soil. At normal temperature and pressure, nitrous oxide is a colorless, odorless gas. Dissolved in water, it tastes slightly sweet. Because of its chemical formula, it is a source of oxygen that may be useful in electronics, for depositions in the gaseous phase and as an oxidant to improve gas-fueled engines performance.