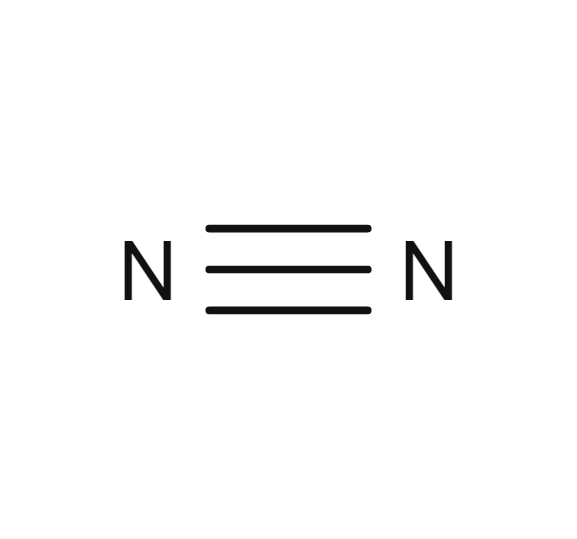
Nitrogen
- N2
- CAS Number 7727-37-9
- UN1066 (gas)
- UN1977 (refrigerated liquid)
Click & drag to move the 3D molecule
Liquid / Gas Volumes
Calculate the volume or mass of a quantity of gas or liquid
Liquid Phase
At boiling point at 1.013 bar
Gas Phase
In standard conditions (1.013 bar, 15°C)
Physical Properties
Molecule phase diagram showing the transition phases between solid, liquid and gas as a function of temperature and pressure
-
- Molar mass 28.013 g/mol
- Content in dry air 780840.00 ppm
-
Critical Point
- Temperature -146.95 °C
- Pressure 34 bar
- Density 314.02 kg/m³
-
Triple Point
- Temperature -210.00 °C
- Pressure 1.252E-1 bar
Pressure 1.013 bar
| Latent heat of fusion (at melting point) | 25.702 kJ/kg |
| Melting point | - 210 °C |
Pressure 1.013 bar
| Boiling point | - 195.8 °C |
| Latent heat of vaporization (at boiling point) | 199.18 kJ/kg |
| Liquid density (at boiling point) | 806.11 kg/m3 |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.9954E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.4019 |
| Gas density (at boiling point) | 4.611 kg/m3 |
| Gas density | 1.2501 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 644.84 vol/vol |
| Heat capacity Cp | 1.0414 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 7.4291E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Specific gravity | 0.97 |
| Specific volume | 0.8 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 24.001 mW/(m.K) |
| Viscosity | 1.6629E-4 Po |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.9971E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.4015 |
| Gas density | 1.1848 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 680.38 vol/vol |
| Heat capacity Cp | 1.0414 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 7.4301E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Solubility in water | 1.386E-5 mol/mol |
| Specific gravity | 0.97 |
| Specific volume | 8.44E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 25.108 mW/(m.K) |
| Viscosity | 1.7339E-4 Po |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.998E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.4013 |
| Gas density | 1.145 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 704.03 vol/vol |
| Heat capacity Cp | 1.0414 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 7.4316E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Solubility in water | 1.183E-5 mol/mol |
| Specific gravity | 0.97 |
| Specific volume | 8.734E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 25.835 mW/(m.K) |
| Viscosity | 1.7805E-4 Po |
Applications
Examples of uses of this molecule in Industry and Healthcare

Aeronautics
Nitrogen is used for heat treatment, welding or laser cutting. Nitrogen-filled tires have an increased lifetime.
Automotive
Nitrogen is used for heat treatment, welding or laser cutting. It also used to produce car pieces with gas assisted injection moulding process. Nitrogen-filled tires have an increased lifetime.

Chemicals
Nitrogen is used directly in chemical process as carrier gas, fluidisation agent or for temperature control and catalyst preparation. It also takes part in several applications in a petrochemical site: for blanketing, drying, purging, stirring, etc.
Electronic components
Nitrogen is used to provide an inert atmosphere, and is used for purging lines and chambers. Nitrogen is also used to carry / dilute materials into chambers. Nitrogen is used as a gas ballast for vacuum pumps.

Food
Nitrogen is used to chill, freeze or control temperature of food products. It allows to control temperature during transportation and distribution with indirect liquid nitrogen injection. Nitrogen preserves and protects foods with Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) to minimize oxidation, micro-organism growth or package collapse. It is also used to protect liquid foods from oxidation through inerting, pressure transfer and deoxigenation.

Glass
In glass production process, nitrogen is used to dilute the hydrogen in the reductive atmosphere needed over the tin bath.

Hospital care
Nitrogen is used in dermatology and for cryo-preservation.

Laboratories & Research Centers
Nitrogen is used to purge, dry or blanket analyzers or chemical reactors (under gaseous state or at low temperature liquid state). Nitrogen can also be used as a carrier gas in gas chromatography for various industrial and hospital analyses and quality control. It is also a balance gas of the calibration gas mixtures for environmental monitoring systems and industrial hygiene gas mixtures.

Metal fabrication
Nitrogen is used for heat treatment and laser cutting.

Metal
Nitrogen is used for inerting and stirring in many applications.

Oil & Gas
For storage tanks and pipeline, nitrogen protects products and facilities (blanketing and inerting). It is also used in operations of snubbing/pigging, pipeline purging, cleanouts and leak test. For overbalanced drilling, nitrogen is used for gas lifting, fracking or fracturing.

Other
Nitrogen is used in heat treatment of various metals. It is a component of the mixtures used in carbon dioxide lasers. It is also used for pneumatic transportation of powdered flammable materials (charcoal).

Pharma & Biotech
Nitrogen is used for inerting, cryo-grinding, lyophilisation, drying, liquid phase transfer of products or synthesis intermediates. It is also used for cryo-condensation of waste gases and low temperature storage.
Safety & Compatibility
GHS04
Gas under pressure
Other Hazards
Asphyxiant in high concentrations. Nitrogen, when in liquid or vapor state at cryogenic temperature can cause cryogenic burns on skin due to cold, which are very similar to a thermal burn.
Metals
| Aluminium | Satisfactory |
| Brass | Satisfactory |
| Monel | No data |
| Copper | No data |
| Ferritic Steel | Satisfactory |
| Stainless steel | Satisfactory |
| Zinc | No data |
| Titanium | No data |
Plastics
| Polytetrafluoroethylene | Satisfactory |
| Polychlorotrifluoroethylene | Satisfactory |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride | Satisfactory |
| Polyvinyl chloride | Satisfactory |
| Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene | No data |
| Polycarbonate | No data |
| Polyamide | Satisfactory |
| Polypropylene | Satisfactory |
Elastomers
| Butyl (isobutene- isoprene) rubber | Satisfactory |
| Nitrile rubber | Satisfactory |
| Chloroprene | Satisfactory |
| Chlorofluorocarbons | No data |
| Silicone | Satisfactory |
| Perfluoroelastomers | Satisfactory |
| Fluoroelastomers | Satisfactory |
| Neoprene | No data |
| Polyurethane | Satisfactory |
| Ethylene-Propylene | Satisfactory |
Lubricants
| Hydrocarbon based lubricant | Satisfactory |
| Fluorocarbon based lubricant | Satisfactory |
Materials compatibility
Learn More
More information
Nitrogen was discovered in 1772 by Daniel Rutherford who called it "noxious air" or "fixed air". Antoine Laurent de Lavoisier isolated it in 1786. The name nitrogen comes from Latin "nitrogenium", where "nitrum" (from Greek nitron) means "saltpetre", and "genes" means "forming". Nitrogen is an inert gas with many industrial applications. It is liquefied by cooling at -320.8 °F (-196 °C/77.15 K). It is mainly found in the atmosphere, where it accounts for 78 % by volume of the air we breath. But nitrogen is also found in the Earth's crust (to a limited extent: in the form of nitrates, etc.), in organic form (in the living or dead plants and organisms), in mineral form (ammonia), thus contributing to soil fertility. In gaseous form, nitrogen is a neutral and colorless gas.