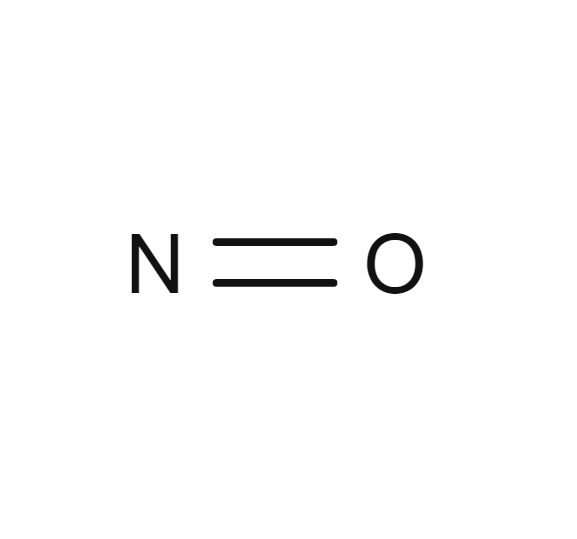
Nitric oxide
- NO
- CAS Number 10102-43-9
- UN1660 (gas)
Click & drag to move the 3D molecule
Liquid / Gas Volumes
Calculate the volume or mass of a quantity of gas or liquid
Liquid Phase
At boiling point at 1.013 bar
Gas Phase
In standard conditions (1.013 bar, 15°C)
Physical Properties
Molecule phase diagram showing the transition phases between solid, liquid and gas as a function of temperature and pressure
-
- Molar mass 30.006 g/mol
- Content in dry air 0.03 ppm
-
Critical Point
- Temperature -93.00 °C
- Pressure 64.8 bar
- Density 517.35 kg/m³
-
Triple Point
- Temperature -163.65 °C
- Pressure 2.189E-1 bar
Pressure 1.013 bar
| Latent heat of fusion (at melting point) | 76.684 kJ/kg |
| Melting point | - 161 °C |
Pressure 1.013 bar
| Boiling point | - 151.77 °C |
| Latent heat of vaporization (at boiling point) | 450.877 kJ/kg |
| Liquid density (at boiling point) | 1280.84 kg/m3 |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 955.71 vol/vol |
| Specific gravity | 1.04 |
| Thermal conductivity | 23.703 mW/(m.K) |
| Viscosity | 1.7804E-4 Po |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 955.71 vol/vol |
| Solubility in water | 4.163E-5 mol/mol |
| Specific gravity | 1.04 |
| Thermal conductivity | 24.859 mW/(m.K) |
| Viscosity | 1.8603E-4 Po |
| Gas/(liquid at boiling point) equivalent | 955.71 vol/vol |
| Solubility in water | 3.477E-5 mol/mol |
| Specific gravity | 1.04 |
| Thermal conductivity | 25.622 mW/(m.K) |
| Viscosity | 1.9126E-4 Po |
Applications
Examples of uses of this molecule in Industry and Healthcare

Hospital care
Nitric oxide is used in ressucitation

Laboratories & Research Centers
Nitric oxide is used in calibration gas mixtures for petrochemical industry, environmental emission monitoring, industrial hygiene monitors and trace impurity analyzers.
Safety & Compatibility
GHS03
Oxidising
GHS04
Gas under pressure
GHS05
Corrosive
GHS06
Acute Toxicity
Threshold of toxicity
| ILV-8h EU (at Patm and 293.15 K) | 2.5 mg/m3 or 2 ppm |
| PEL USA OSHA (vol) | 25 ppm |
| VLEP 8h France (at Patm and 293.15 K) | 2.5 mg/m3 or 2 ppm |
Odor
Slightly irritating
Metals
| Aluminium | Not recommended |
| Brass |
Risk of stress corrosion cracking
Not recommended
|
| Monel | No data |
| Copper | No data |
| Ferritic Steel | Satisfactory |
| Stainless steel | Satisfactory |
| Zinc | No data |
| Titanium | No data |
Plastics
| Polytetrafluoroethylene |
Dangerous product release
Acceptable
|
| Polychlorotrifluoroethylene |
Dangerous product release
Acceptable
|
| Polyvinylidene fluoride |
Dangerous product release
Acceptable
|
| Polyvinyl chloride |
Violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
| Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene | No data |
| Polycarbonate | No data |
| Polyamide |
Violent reaction (oxidation/burning), significant loss of mass
Not recommended
|
| Polypropylene |
Violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
Elastomers
| Butyl (isobutene- isoprene) rubber |
Significant loss of mass; violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
| Nitrile rubber |
Significant loss of mass; violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
| Chloroprene |
Significant loss of mass, violent reaction (oxidation/burning), dangerous product release
Not recommended
|
| Chlorofluorocarbons | No data |
| Silicone |
violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
| Perfluoroelastomers |
Dangerous product release
Acceptable
|
| Fluoroelastomers |
Dangerous product release
Acceptable
|
| Neoprene | No data |
| Polyurethane |
Dangerous product release
Acceptable
|
| Ethylene-Propylene |
Significant loss of mass; violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
Lubricants
| Hydrocarbon based lubricant |
Contamination of the material; violent reaction (oxidation/burning)
Not recommended
|
| Fluorocarbon based lubricant |
Contamination of the material, dangerous product release
Not recommended
|
Materials compatibility
Learn More
More information
Nitric oxide is a major air pollutant, mainly rejected by premises heating systems, cars, thermal power plants and incineration plants.