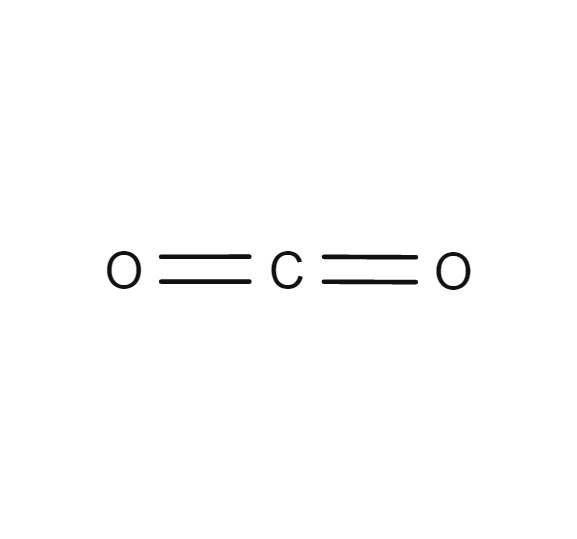
Carbon dioxide
- CO2
- CAS Number 124-38-9
- UN1013 (gas)
- UN2187 (refrigerated liquid)
- UN1845 (solid)
Click & drag to move the 3D molecule
Liquid / Gas Volumes
Calculate the volume or mass of a quantity of gas or liquid
Liquid Phase
At boiling point at 1.013 bar
Gas Phase
In standard conditions (1.013 bar, 15°C)
Physical Properties
Molecule phase diagram showing the transition phases between solid, liquid and gas as a function of temperature and pressure
-
- Molar mass 44.010 g/mol
- Content in dry air 400.00 ppm
-
Critical Point
- Temperature 31.06 °C
- Pressure 73.83 bar
- Density 468.19 kg/m³
-
Triple Point
- Temperature -56.56 °C
- Pressure 5.1867 bar
At triple point
| Latent heat of fusion | 204.93 kJ/kg |
| Temperature of the triple point | - 56.57 °C |
| Liquid density (at triple point) | 1178.4 kg/m3 |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.9326E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.3083 |
| Gas density | 1.9763 kg/m3 |
| Heat capacity Cp | 8.2684E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 6.3202E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Specific gravity | 1.53 |
| Specific volume | 5.06E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 14.674 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 34.9054 bar |
| Viscosity | 1.3711E-4 Po |
| Temperature of the sublimation point | - 78.45 °C |
| Gas density (at sublimation point) | 2.8179 kg/m3 |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.9435E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.2995 |
| Gas density | 1.8714 kg/m3 |
| Heat capacity Cp | 8.4124E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 6.4738E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Solubility in water | 8.21E-4 mol/mol |
| Specific gravity | 1.53 |
| Specific volume | 5.344E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 15.844 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 50.9921 bar |
| Viscosity | 1.4446E-4 Po |
| Compressibility factor Z | 9.9496E-1 |
| Cp/Cv ratio γ | 1.2941 |
| Gas density | 1.8075 kg/m3 |
| Heat capacity Cp | 8.5085E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Heat capacity Cv | 6.5749E-1 kJ/(kg.K) |
| Solubility in water | 6.15E-4 mol/mol |
| Specific gravity | 1.53 |
| Specific volume | 5.532E-1 m3/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 16.643 mW/(m.K) |
| Vapor pressure | 64.4789 bar |
| Viscosity | 1.4932E-4 Po |
Applications
Examples of uses of this molecule in Industry and Healthcare

Aeronautics
Carbon dioxide is used as a shielding gas for arc welding. Dry Ice (Solid carbon dioxide) is used to remove particles and organic residues from metals, polymers, ceramics and glasses. Calibrated mixtures of carbon dioxide and nitrogen are used for the calibration of measuring equipments used for engine test emissions.
Automotive
Carbon dioxide is used as a shielding gas for arc welding. Dry Ice cleaning removes particles and organic residues from metals, polymers, ceramics, glasses. Calibrated mixtures of carbon dioxyde and nitrogen are used for the calibration of measuring equipments used for engine test emissions.

Beverage
Carbon dioxide is used to carbonate beverages such as soft drinks, mineral water or beer and for wine maturation. Carbonic ice (also called dry ice) is used at difference stages of production and distribution of beverages. Supercritical carbon dioxide is used to extract caffein from coffee beans.

Chemicals
Carbon dioxide is used as a raw material in chemical process like urea or methionine synthesis. Carbon dioxide is used in chemistry for controlling reactor temperatures. CO2 is also employed to neutralize alkaline effluents. Carbon dioxide is used under supercritical conditions for purifying or dyeing polymers, animal or vegetal fibers.
Electronic components
Carbon dioxide is used for cleaning wafers.

Waste & Water management
Carbon dioxide is broadly used in water management to control pH, and is a very good alternative to sulfuric or hypochlorous/hydrochloric acid as it is economic, safe and environmental friendly. Combined with lime it is used in desalination plants for potable water production.

Food
The food industry employs carbon dioxide for food processing applications such as chilling and freezing, modified atmosphere packaging and temperature control for products being stored and transported. Carbon dioxide increases the life of many food products thanks to it fungistatic and bacteriostatic properties. Food products are conditioned under Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP). Carbon dioxide is also used in greenhouses to boost a plant growth..

Hospital care
Carbon dioxide is used in surgery as an insufflated gas and in dermatology.

Laboratories & Research Centers
Carbon dioxide is used mainly in its supercritical state as mobile phase in both chromatography and extraction applications (for purification in food or health). Dry ice (carbon dioxide in solid phase) is used for research purposes in laboratories. Carbon dioxide is also used in gas mixture for calibration of analysers monitoring air quality and CO2 emissions.

Metal
In metal industry, CO2 is typically used for environment protection, specifically in fume suppression in Electric Arc Furnace and the non ferrous metallurgy operations. Liquid CO2 can be used to treat waters from Acid Mine Drainage to recover rare earth element carbonates of high value. CO2 is also used in lasers.

Oil & Gas
Carbon dioxide is used to enhance oil recovery (EOR) as it mixes with heavy oils and reduces their viscosity. It can also be used to repressurize depleted oil reservoirs. When anthropogenic CO2 (i.e. CO2 from human activity) is used for EOR, some CO2 remains stored in the reservoir, partially reducing the overall impact of the fossil fuel on global warming.

Pharma & Biotech
Supercritical carbon dioxide is used to extract components (oils) from natural products. It is used to control the atmosphere (inerting) of processes. Carbon dioxide is a reactant in chemical synthesis. It is also used to transport products at low temperature down to: -78°C/-108.4°F/195.15K.
Safety & Compatibility
GHS04
Gas under pressure
Threshold of toxicity
| ILV-8h EU (at Patm and 293.15 K) | 9000 mg/m3 or 5000 ppm |
| PEL USA OSHA (vol) | 5000 ppm |
Odor
none
Metals
| Aluminium | Satisfactory |
| Brass | Satisfactory |
| Monel | No data |
| Copper | No data |
| Ferritic Steel |
Risk of stress corrosion cracking in presence of CO and water
Acceptable
|
| Stainless steel | Satisfactory |
| Zinc | No data |
| Titanium | No data |
Plastics
| Polytetrafluoroethylene | Satisfactory |
| Polychlorotrifluoroethylene | Satisfactory |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride | Satisfactory |
| Polyvinyl chloride | Satisfactory |
| Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene | No data |
| Polycarbonate | No data |
| Polyamide | Satisfactory |
| Polypropylene | Satisfactory |
Elastomers
| Butyl (isobutene- isoprene) rubber |
significant swelling
Not recommended
|
| Nitrile rubber |
Significant swelling, change of mechanical properties
Not recommended
|
| Chloroprene |
Significant swelling, change of mechanical properties
Not recommended
|
| Chlorofluorocarbons | No data |
| Silicone |
Strong rate of permeation
Acceptable
|
| Perfluoroelastomers |
Significant swelling, change of mechanical properties
Not recommended
|
| Fluoroelastomers |
Significant swelling, change of mechanical properties
Not recommended
|
| Neoprene | No data |
| Polyurethane | Satisfactory |
| Ethylene-Propylene |
Significant loss of mass and swelling
Acceptable
|
Lubricants
| Hydrocarbon based lubricant | Satisfactory |
| Fluorocarbon based lubricant | Satisfactory |
Materials compatibility
Learn More
More information
Jean-Baptiste Van Helmont, a Flemisch chemist and physicist of the 17th century observed that the burning of wood coal in a closed vessel produces ashes of a mass inferior to the material introduced. His conclusion is that coal has been transformed into some invisible substance he called "gas". Carbon dioxide gas is formed by two elements: carbon and oxygen. Carbon dioxide is a part of Natural Carbon Cycle (NCC) where carbon dioxide is exchanged among three main carbon pools – land, atmosphere and ocean. The process, where carbon dioxide is consumed by plants and other organisms and converted into biomass is called photosynthesis. The process where CO2 is released by living species (humans, animals, plants) is called respiration. Apart of NCC there is an Anthropogenic Carbon Cycle (ACC or Manmade Carbon Cycle) where fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, crude oil) or biomass are burned to produce energy and carbon dioxide is released. Carbon dioxide is an essential gas for life. It functions as a Green House Gas (GHG) maintaining livable conditions on Earth. Carbon dioxide gas has a slightly irritating odor, is colorless and heavier than air. It freezes at -78.5 °C to form carbon dioxide snow, used in fired extinguishers.